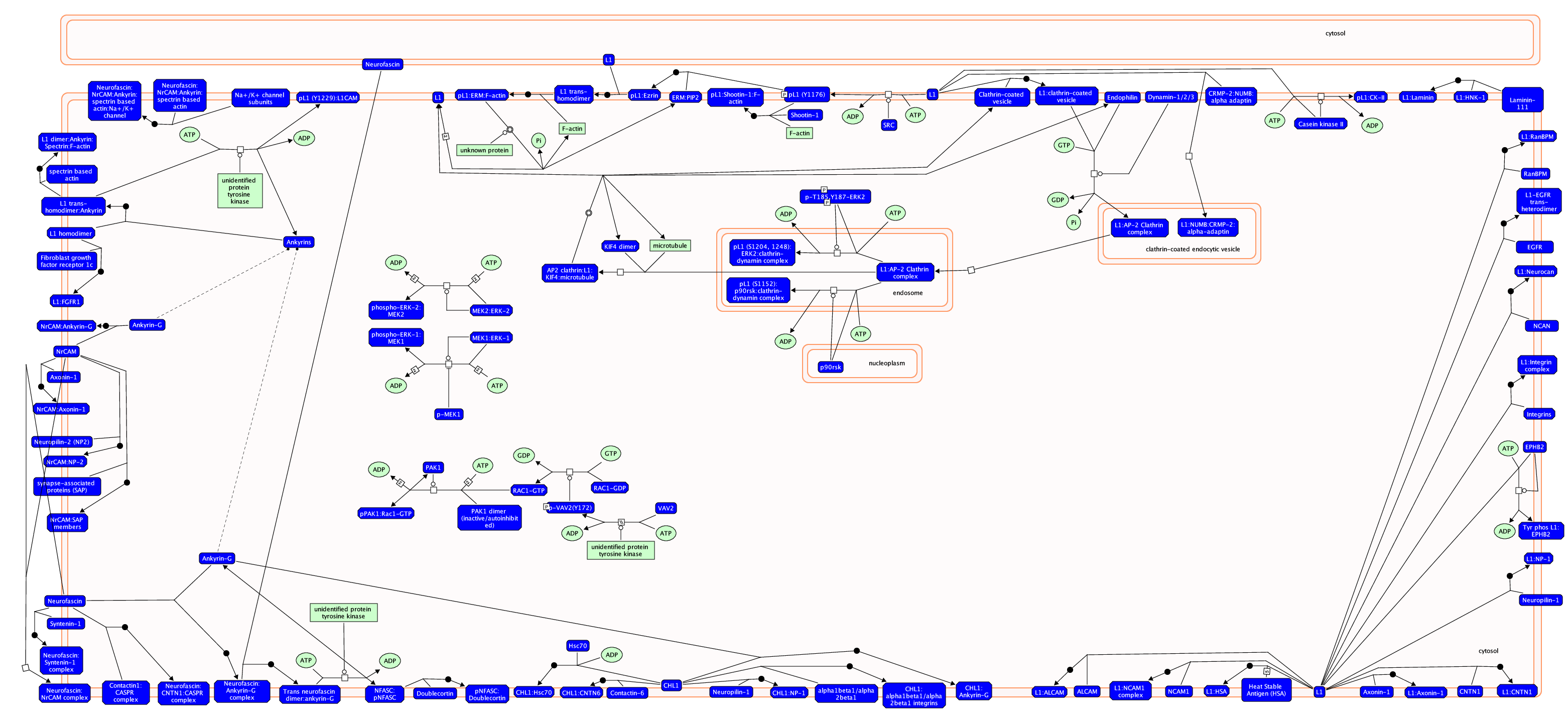
L1CAM相互作用信号通路介绍
The L1 family of cell adhesion molecules (L1CAMs) are a subfamily of the immunoglobulin superfamily of transmembrane receptors, comprised of four structurally related proteins: L1, Close Homolog of L1 (CHL1), NrCAM, and Neurofascin. These CAMs contain six Ig like domains, five or six fibronectin like repeats, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic domain. The L1CAM family has been implicated in processes integral to nervous system development, including neurite outgrowth, neurite fasciculation and inter neuronal adhesion.
L1CAM members are predominately expressed by neuronal, as well as some nonneuronal cells, during development. Except CHL1 all the other members of L1 family contain an alternatively spliced 12-nclueotide exon, encoding the amino acid residues RSLE in the neuronal splice forms but missing in the non-neuronal cells. The extracellular regions of L1CAM members are divergent and differ in their abilities to interact with extracellular, heterophilic ligands. The L1 ligands include other Ig-domain CAMs (such as NCAM, TAG-1/axonin and F11), proteoglycans type molecules (neurocan), beta1 integrins, and extra cellular matrix protein laminin, Neuropilin-1, FGF and EGF receptors. Some of these L1-interacting proteins also bind to other L1CAM members. For example TAG-1/axonin interact with L1 and NrCAM; L1, neurofascin and CHL1 binds to contactin family members. The cytoplasmic domains of L1CAM members are most highly conserved. Nevertheless, they have different cytoplasmic binding partners, and even those with similar binding partners may be involved in different signaling complexes and mechanisms. The most conserved feature of L1CAMs is their ability to interact with the actin cytoskeletal adapter protein ankyrin. The cytoplasmic ankyrin-binding domain, exhibits the highest degree of amino acid conservation throughout the L1 family.
基因功能分类
| cell adhesion | CD24, CHL1, CNTN1, NCAN, ALCAM, CNTN6, LAMA1, ITGA2, ITGA2B, ITGA5, ITGA9, ITGAV, ITGB3, L1CAM, LAMB1, LAMC1, NCAM1, RAC1, CNTN2, CNTNAP1, NRP2 |
| cell-matrix adhesion | ITGA1, ITGA2, ITGA2B, ITGAV, ITGB1, ITGB3, RAC1, CNTN2 |
| ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | ANK1, ANK2, ANK3, SPTBN5, SPTBN4, SPTA1, SPTAN1, SPTB, SPTBN1, SPTBN2 |
| extracellular matrix organization | NCAN, LAMA1, ITGA1, ITGA2, ITGA2B, ITGA5, ITGA9, ITGAV, ITGB1, ITGB3, LAMB1, LAMC1 |
| MAPK cascade | DLG4, EGFR, FGFR1, NCAM1, PAK1, SPTBN5, MAPK1, MAPK3, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, SPTBN4, SPTA1, SPTAN1, SPTB, SPTBN1, SPTBN2 |
| nervous system development | DCX, DLG1, DLG3, DLG4, DPYSL2, EPHB2, KCNQ2, L1CAM, SCN2B, SCN3A |
参考文献
- Herron LR, Hill M, Davey F, Gunn-Moore FJ. The intracellular interactions of the L1 family of cell adhesion molecules. Biochem J. 2009 May 1;419(3):519-31
- Schmid RS, Maness PF. L1 and NCAM adhesion molecules as signaling coreceptors in neuronal migration and process outgrowth. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008 Jun;18(3):245-50
- Maness PF, Schachner M. Neural recognition molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily: signaling transducers of axon guidance and neuronal migration. Nat Neurosci. 2007 Jan;10(1):19-26
- Kamiguchi H. The mechanism of axon growth: what we have learned from the cell adhesion molecule L1. Mol Neurobiol. 2003 Dec;28(3):219-28
- Kamiguchi H, Lemmon V. Neural cell adhesion molecule L1: signaling pathways and growth cone motility. J Neurosci Res. 1997 Jul 1;49(1):1-8
服务条款
发货速度
现货:订单核实后5个工作日内发货;
定制:15-20个工作日。